Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA)
A sleep disorder that causes repeated breathing interruptions during sleep.
Request An AppointmentRefer A Patient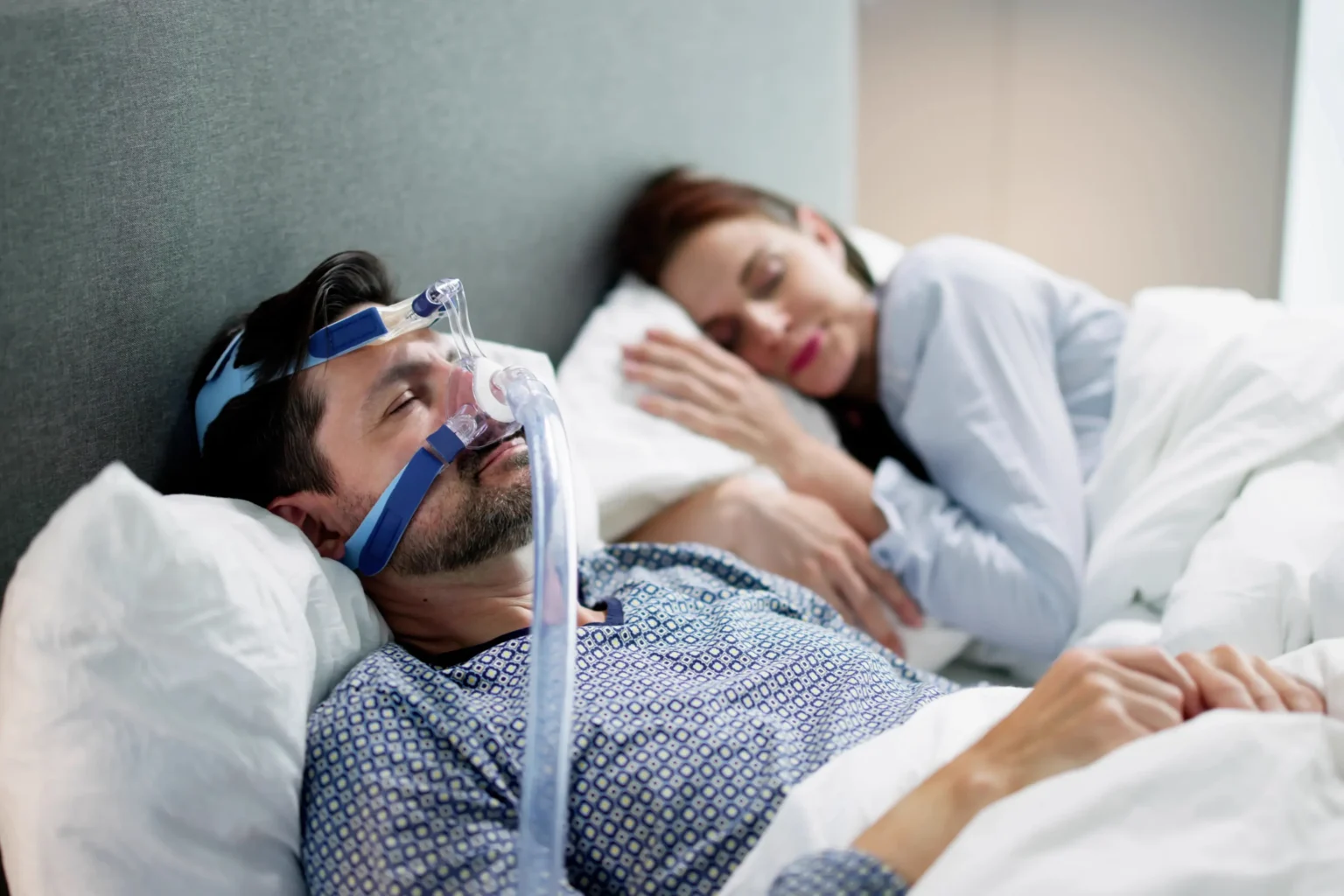
What is Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
Table Of Contents
Causes and Risk Factors
OSA occurs when the airway becomes blocked during sleep. Several factors can contribute to this obstruction, including:
- Excess weight and obesity
- Enlarged tonsils or adenoids
- A naturally narrow airway
- Nasal congestion or obstruction
- Smoking and alcohol use
- Family history of OSA

Symptoms of OSA
- Loud snoring
- Gasping or choking during sleep
- Excessive daytime sleepiness
- Morning headaches
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability or mood changes
Symptoms may vary, and some individuals may not be aware of their disrupted breathing during sleep.
Health Complications Linked to OSA
Untreated OSA can contribute to severeserious health conditions, such as:
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Type 2 diabetes
- Depression and anxiety
- Increased risk of motor vehicle accidents due to daytime drowsiness
Diagnosis and Evaluation
A sleep study is the primary method for diagnosing OSA. This can be conducted in a sleep lab or at home with a home sleep apnea test. These studies monitor breathing patterns, oxygen levels, and other physiological markers during sleep. A board-certified sleep medicine physician evaluates the results to determine the severity of OSA and recommend appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options
Treatment for OSA focuses on keeping the airway open during sleep. Options may include:
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): CPAP therapy provides a steady stream of air through a mask to keep the airway open.
- Bilevel Positive Airway Pressure (BiPAP): Similar to CPAP, BiPAP delivers different air pressures for inhalation and exhalation, making it easier to breathe out.
- Automatic Positive Airway Pressure (APAP): APAP adjusts pressure levels automatically throughout the night based on breathing patterns.
- Oral Appliances: Custom-fitted devices reposition the jaw to maintain an open airway.
- Surgical Options: In cases where other treatments are ineffective, procedures to remove or alter airway obstructions may be considered.
Lifestyle Modifications for OSA Management:
These are not just suggestions, but powerful tools in your hands to manage OSA effectively:
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce airway obstruction.
- Sleep Position Adjustment: Sleeping on the side instead of the back may help prevent airway collapse.
- Limiting Alcohol and Sedatives: These substances relax throat muscles and can worsen symptoms.
- Addressing Nasal Congestion: Treating allergies or nasal obstruction can improve airflow during sleep.
Frequently Asked Questions
0
How is OSA different from simple snoring?
Snoring can be a symptom of OSA, but not everyone who snores has the condition. OSA involves breathing interruptions and oxygen level drops, which can lead to serious health risks.
0
Can OSA be treated without a CPAP machine?
While CPAP is the most effective treatment, alternative options like oral appliances, lifestyle modifications, and surgery may be considered based on the severity of the condition.
0
What are the long-term risks of untreated OSA?
Untreated OSA can contribute to heart disease, high blood pressure, stroke, and metabolic disorders, making early diagnosis and treatment essential. This knowledge should motivate you to take action for your health.
0
Is a home sleep apnea test as accurate as an in-lab study?
Home tests are convenient and effective for many patients, but in-lab studies provide a more comprehensive evaluation when additional monitoring is needed.

